The propeller shaft (drive shaft or tail shaft) is used to transmit the movement mechanism in vehicles. Since it can move in more than one axis, it has the ability to absorb the stress on the shaft. This system, which we usually see in wheeled vehicles, is also used in different places where there are boats or internal combustion engines. You can find the videos and resources I used while preparing this article at the end of the article.
The purpose of this article is to inform the user about the propeller shaft in general.

What is Propeller Shaft
You may have wondered how the motion produced in the engine is transmitted to the wheels. Everything has been thought of in these systems, down to the smallest detail. The rotational movement that occurs with the start of the engine is transferred to the propeller shaft.
The shaft absorbs the unwanted lateral forces with the moving parts on it and transmits the same movement along the axis to the rear of the car. Let’s find out together how these fast-moving vehicles meet so much torque when cornering and passing over bumps.
Diagram of a Propeller Shaft
For a more detailed representation of the parts, you can refer to the propeller shaft diagram below.
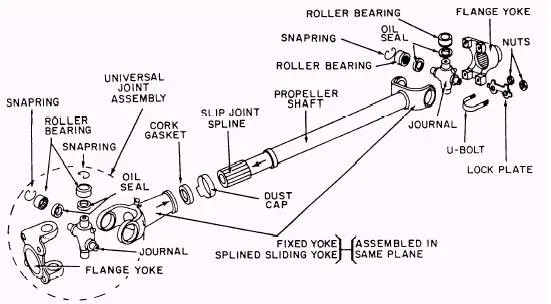
Parts of Propeller Shaft
The shaft consists of many moving parts. Below we have mentioned the parts found in most shaft systems.
Journal – Spider – Cross
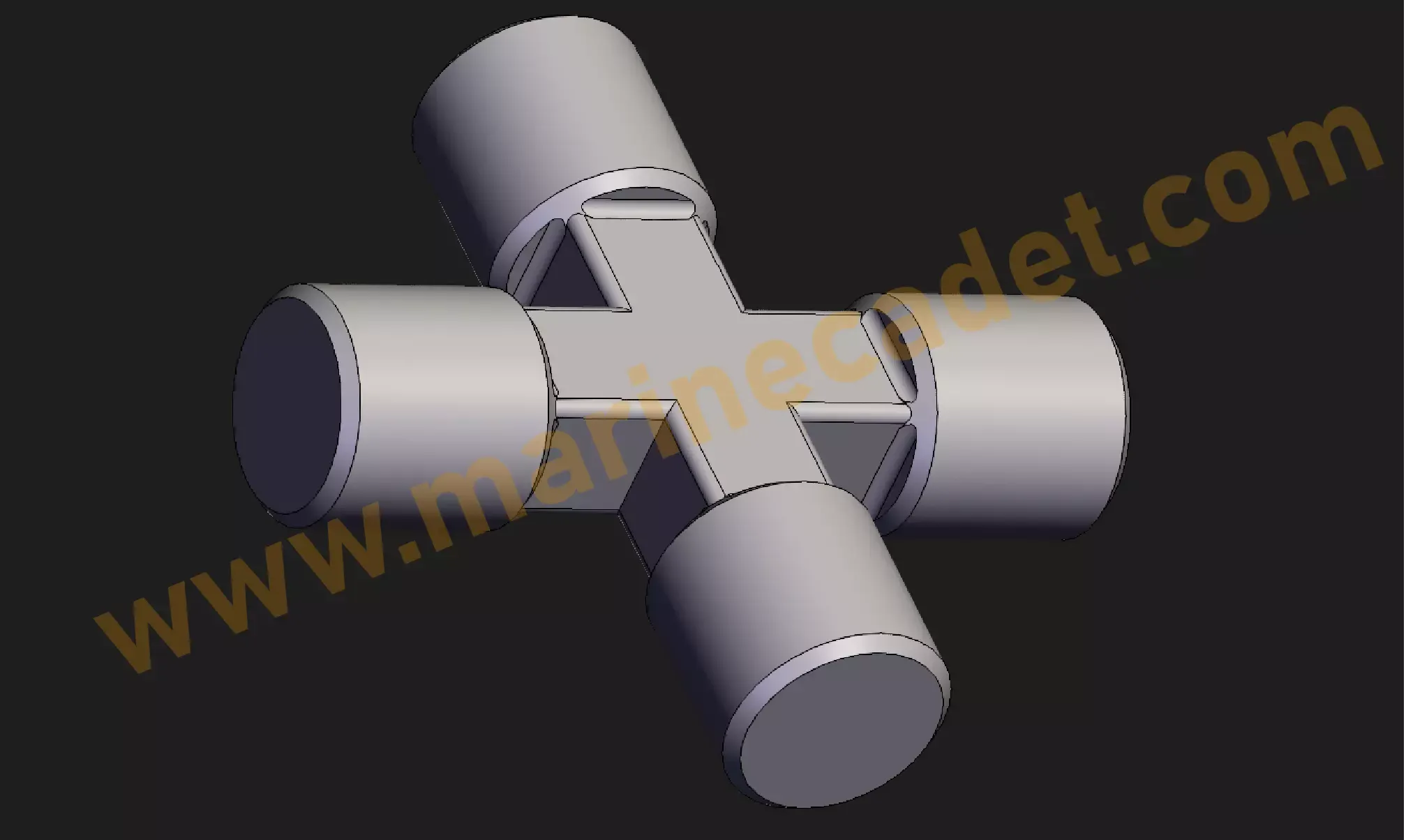
Although this piece is known as U-joint, it may be more appropriate to use it with the names of cross, journal or spider. Because Universal joint is actually the use of yoke and cross piece together. As you can see in the image below, the u-joint allows vehicles to make axial movements while turning and passing over bumps. Just like the bone joint in humans, it facilitates movement in different directions.
It is very important to lubricate this part, because it makes the rotational movement and moves continuously in the x and y axis.
Tube
It is generally located in the middle of the drive shaft and shares the task of transmitting torque. In some systems, pistons are used for suspension in the tube. Thus, the vehicle can extinguish the force on itself when accelerating or braking.
Slip Yoke – Sliding Yoke
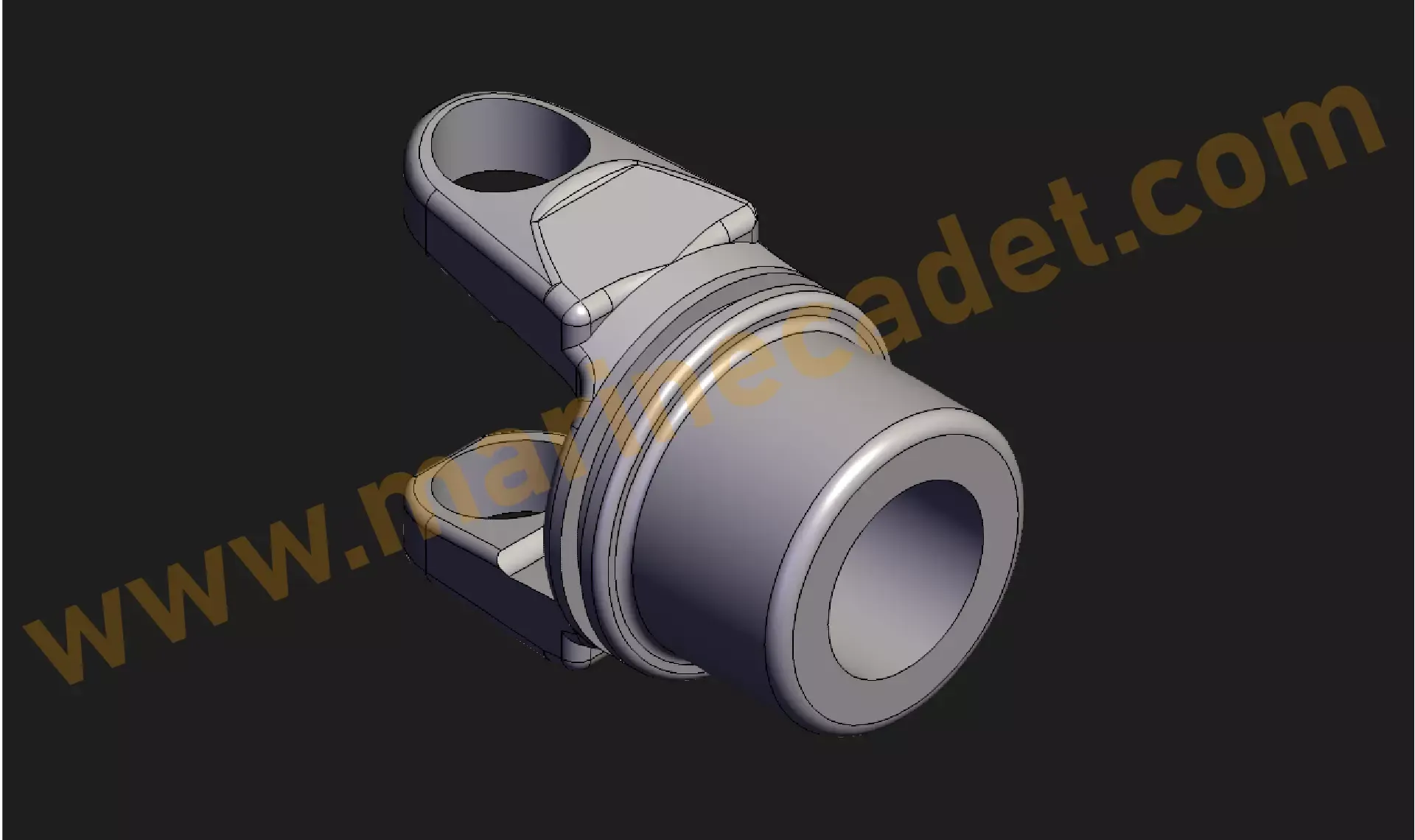

End Yoke or Flange Yoke
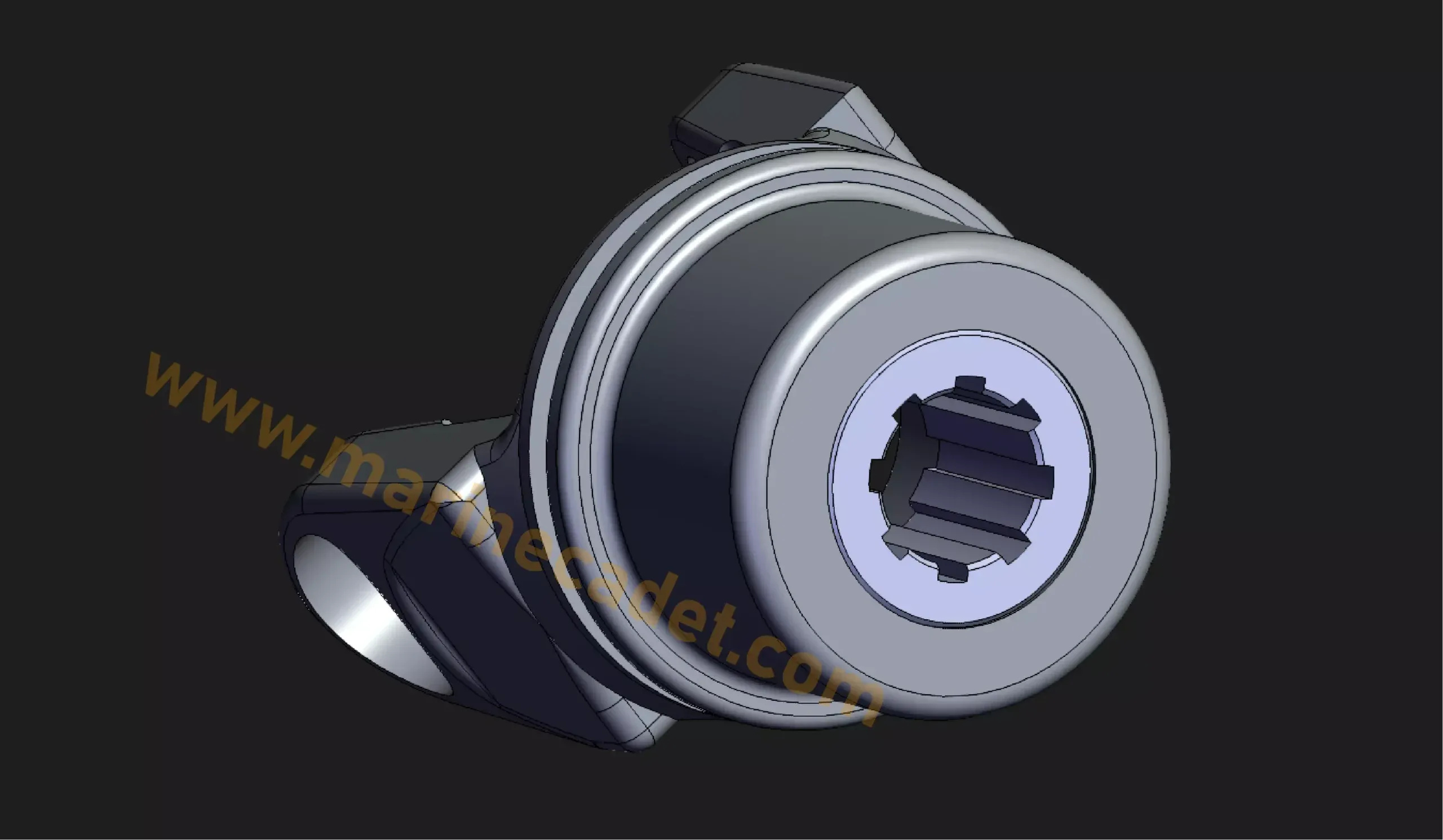
This part is directly connected to the gearbox or differential. It is placed as a visual representation and can be in different shapes. Thanks to the channels inside, it increases the grip of the shaft at high torque.
Universal joint (U-joint)

A universal joint, also known as a U-joint, is a mechanical component that connects the drive shaft or propeller shaft to the differential in a vehicle. It allows for the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels while also allowing for flexibility in movement as the suspension and wheels move up and down.
A U-joint consists of two yokes, each with a trunnion, and a cross-shaped connecting piece called a cross-and-bearing assembly. The trunnions of the yokes are inserted into the ends of the cross-and-bearing assembly, which allows the yokes to rotate and pivot relative to one another.
This allows the drive shaft or propeller shaft to maintain a constant angle and alignment with the differential, even when the suspension and wheels move.
U-joints are commonly used in rear-wheel drive vehicles, but can also be found in front-wheel drive and four-wheel drive vehicles. They are designed to withstand the constant stresses of high-speed driving and heavy loads, but over time they can wear out and require replacement.
Functions of the Propeller Shaft
The Propeller Shaft, also known as the drive shaft, has several key functions in a vehicle:
- Transmitting power: The propeller shaft transmits power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move.
- Maintaining alignment: The propeller shaft helps to maintain the proper alignment between the engine and the wheels, ensuring that power is transmitted efficiently.
- Absorbing vibrations: The propeller shaft acts as a vibration dampener, absorbing vibrations and shocks from the engine and transmission to provide a smoother ride for the vehicle.
- Allowing for suspension movement: The propeller shaft is designed to allow for movement of the suspension and wheels, allowing the vehicle to navigate uneven terrain and bumps in the road without causing damage to the drivetrain.
- Supporting the weight of the vehicle: The propeller shaft also helps to support the weight of the vehicle, distributing the load evenly across the drivetrain.
- Accommodating the different angles: The propeller shafts can also be equipped with a universal joint to accommodate the different angles between the engine and the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move in different directions.
Materials Used in Propeller Shaft
Drive propeller shafts are typically made from a variety of materials, including:
- Carbon steel: This is a strong and durable material that is commonly used in the construction of drive propeller shafts. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to work with, making it a popular choice among manufacturers.
- Aluminum: This lightweight metal is often used in high-performance vehicles to reduce the overall weight of the drivetrain. It also offers good corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity.
- Stainless steel: This type of steel is known for its corrosion resistance and durability. It is often used in marine and off-road applications where the drive propeller shaft is exposed to harsh environments.
- High-strength alloys: These alloys, such as titanium and Inconel, offer high strength and durability while also being lightweight. They are often used in high-performance and racing applications where maximum strength and minimal weight are crucial.
- Composite materials: Some manufacturers are also experimenting with using composite materials such as carbon fiber or glass fiber reinforced plastics to make drive propeller shafts. These materials offer high strength and durability while also being lightweight.
Types of Propeller Shaft
There are several types of propeller shafts, each with their own unique characteristics and uses:
- Single piece propeller shaft: A single piece propeller shaft is a single, continuous shaft that connects the transmission to the differential. It is the simplest and most common type of propeller shaft.
- Two-piece propeller shaft: A two-piece propeller shaft is made up of two separate pieces, one connected to the transmission and the other to the differential. This type of propeller shaft is used in vehicles with a long wheelbase and is designed to accommodate suspension movement and different angles between the transmission and differential.
- Three-piece propeller shaft: A three-piece propeller shaft is made up of three separate pieces, two of which are connected to the transmission and the differential, while the third connects the two. This type of propeller shaft is used in vehicles with a longer wheelbase and is designed to accommodate suspension movement and different angles between the transmission and differential.
- Constant velocity propeller shaft: A constant velocity propeller shaft is a type of drive shaft that uses a series of universal joints to accommodate the different angles between the transmission and differential. It is designed to allow for a smooth transfer of power even when the suspension and wheels are moving.
- Cardan propeller shaft: A cardan propeller shaft is a type of drive shaft that uses a universal joint to connect the transmission to the differential. It allows for the transfer of power while also allowing for flexibility in movement as the suspension and wheels move up and down.
- Rigid propeller shaft: A rigid propeller shaft is a drive shaft that has no flexibility and is used in vehicles with a short wheelbase or where the transmission and differential are in close proximity to each other.
Advantages of using a propeller shaft
- Increased power transmission: A drive propeller shaft allows for efficient power transmission from the engine to the wheels, providing better vehicle performance and acceleration.
- Reduced vibration: A drive propeller shaft helps to reduce vibrations that can be caused by the engine and transmission, providing a smoother ride for the vehicle.
- Increased durability: Drive propeller shafts are generally made from high-quality materials that are designed to withstand the stresses of high-speed driving and heavy loads.
Disadvantages of using a propeller shaft
- Increased maintenance: Drive propeller shafts require regular maintenance and inspection to ensure that they are functioning properly.
- Cost: Drive propeller shafts can be relatively expensive to replace or repair if they become damaged.
- Complexity: Drive propeller shafts are complex mechanical components that can be difficult to diagnose and repair if they malfunction.
- Limited accessibility: In some vehicles, the drive propeller shaft is difficult to access and may require special tools or equipment to repair or replace.